Documentation
Qdrant (read: quadrant) is a vector similarity search engine. Use our documentation to develop a production-ready service with a convenient API to store, search, and manage vectors with an additional payload. Qdrant’s expanding features allow for all sorts of neural network or semantic-based matching, faceted search, and other applications.
Product Release: Announcing Qdrant Hybrid Cloud!
Now you can attach your own infrastructure to Qdrant Cloud!
Use Qdrant Hybrid Cloud to build the best private environment that suits your needs. Manage your own clusters via the Qdrant Cloud UI, but continue to run them within your own private infrastructure for complete security and sovereignty.
First-Time Users:
There are three ways to use Qdrant:
- Run a Docker image if you don’t have a Python development environment. Setup a local Qdrant server and storage in a few moments.
- Get the Python client if you’re familiar with Python. Just
pip install qdrant-client. The client also supports an in-memory database. - Spin up a Qdrant Cloud cluster: the recommended method to run Qdrant in production. Read Quickstart to setup your first instance.
Recommended Workflow:
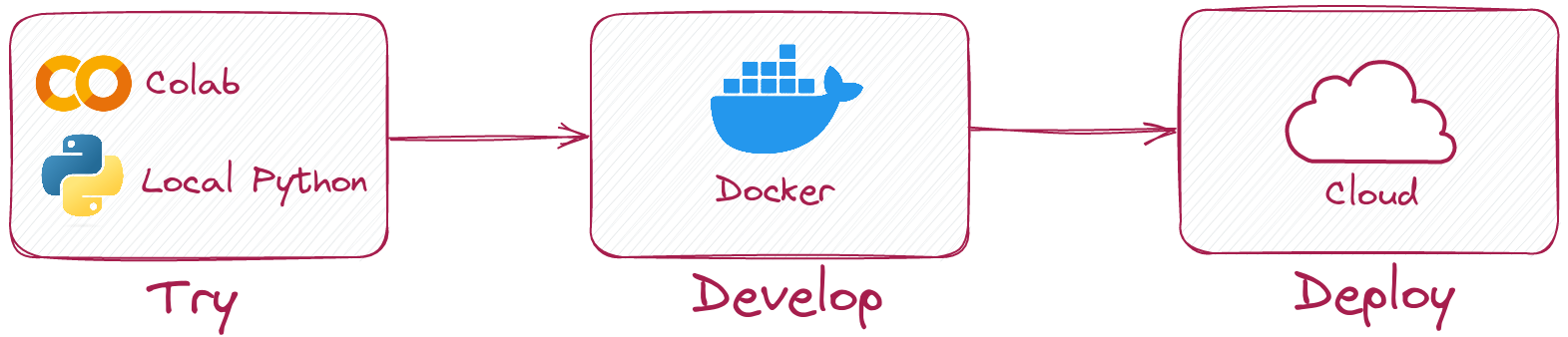
First, try Qdrant locally using the Qdrant Client and with the help of our Tutorials and Guides. Develop a sample app from our Examples list and try it using a Qdrant Docker container. Then, when you are ready for production, deploy to a Free Tier Qdrant Cloud cluster.
Try Qdrant with Practice Data:
You may always use our Practice Datasets to build with Qdrant. This page will be regularly updated with dataset snapshots you can use to bootstrap complete projects.
Popular Topics:
| Tutorial | Description | Tutorial | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Installation | Different ways to install Qdrant. | Collections | Learn about the central concept behind Qdrant. |
| Configuration | Update the default configuration. | Bulk Upload | Efficiently upload a large number of vectors. |
| Optimization | Optimize Qdrant’s resource usage. | Multitenancy | Setup Qdrant for multiple independent users. |
Common Use Cases:
Qdrant is ideal for deploying applications based on the matching of embeddings produced by neural network encoders. Check out the Examples section to learn more about common use cases. Also, you can visit the Tutorials page to learn how to work with Qdrant in different ways.
| Use Case | Description | Stack |
|---|---|---|
| Semantic Search for Beginners | Build a search engine locally with our most basic instruction set. | Qdrant |
| Build a Simple Neural Search | Build and deploy a neural search. Check out the live demo app. | Qdrant, BERT, FastAPI |
| Build a Search with Aleph Alpha | Build a simple semantic search that combines text and image data. | Qdrant, Aleph Alpha |
| Developing Recommendations Systems | Learn how to get started building semantic search and recommendation systems. | Qdrant |
| Search and Recommend Newspaper Articles | Work with text data to develop a semantic search and a recommendation engine for news articles. | Qdrant |
| Recommendation System for Songs | Use Qdrant to develop a music recommendation engine based on audio embeddings. | Qdrant |
| Image Comparison System for Skin Conditions | Use Qdrant to compare challenging images with labels representing different skin diseases. | Qdrant |
| Question and Answer System with LlamaIndex | Combine Qdrant and LlamaIndex to create a self-updating Q&A system. | Qdrant, LlamaIndex, Cohere |
| Extractive QA System | Extract answers directly from context to generate highly relevant answers. | Qdrant |
| Ecommerce Reverse Image Search | Accept images as search queries to receive semantically appropriate answers. | Qdrant |
























